
Cloudflare Down: Why You See “Please Unblock challenges.cloudflare.com to proceed” on ChatGPT and Perplexity
When major parts of the internet suddenly seem inaccessible, the issue often points to a fundamental infrastructure provider. Recently, a significant outage linked to Cloudflare has left countless users unable...
Continue reading

OpenAI Atlas: New ChatGPT Browser Is Here To Revolutionize The Way We Surf the Internet
OpenAI Atlas is a game-changing AI-enhanced browser that has ChatGPT embedded within the web surfing experience. While other browsers use extensions or plug-ins to implement AI capabilities, Atlas is designed...
Continue reading
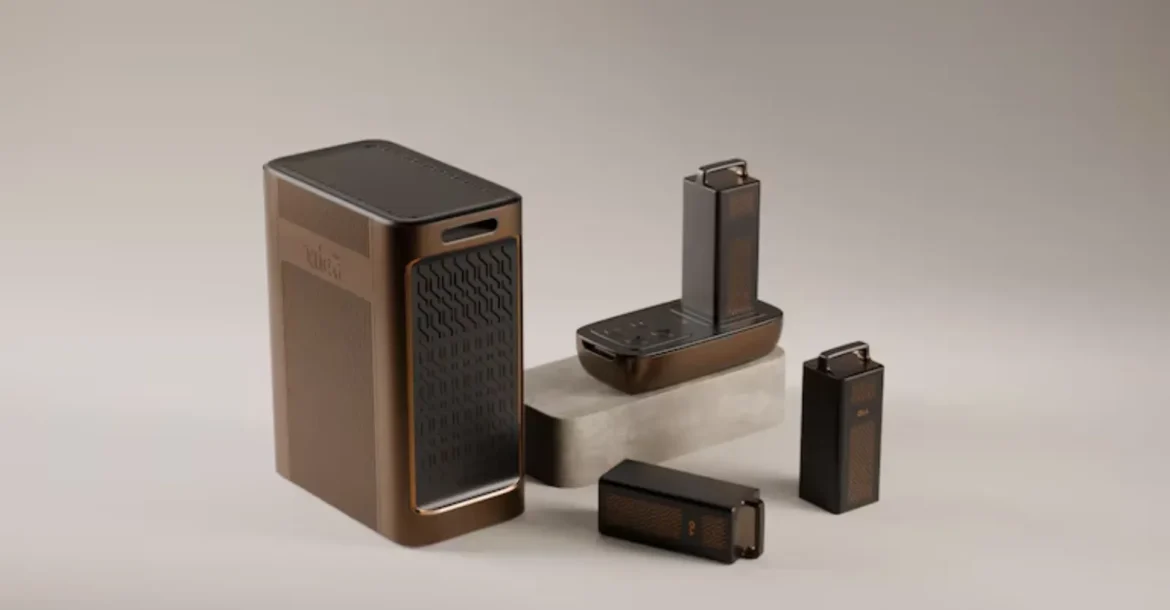

Ola Shakti Energy Storage System: Ola Electric’s Bold Leap Beyond Mobility
Ola Electric has entered the energy storage business formally with the introduction of Ola Shakti, a home Battery Energy Storage System, which is a significant change in the direction of...
Continue reading

How to Install Adobe Photoshop: Step-by-Step Guide
Adobe Photoshop is a potent image editing tool used across the board, from newbies to experts, for graphic design, photo manipulation, and digital art. However, you may face compatibility issues...
Continue reading
DeepSeek: Transforming Global AI Innovation and Ethics
Artificial intelligence keeps evolving to change the world in every conceivable way – a country’s way of life, its industries, or its economy. DeepSeek, a relatively new yet iconic Chinese...
Continue reading
Breaking into AI: Essential Skills and Beginner-Friendly Resources
Artificial intelligence is no longer the stuff of science fiction; rather, it is a pillar upon which groundbreaking innovations are constructed and one that has revolutionized fields ranging from healthcare...
Continue reading

Trump Coin: Market Trends, Controversies, and Future Insights
Trump Coin ($TRUMP) has made its debut on cryptocurrency markets and has sparked widespread discussion across the globe. The phenomenal mix of hype, speculation, and controversy that surfaces with Donald...
Continue reading

How Eskom Powers South Africa’s Future With Renewable Energy
Having been a key player in the development of the power and energy sector of the country over several decades, Eskom has had its dark side of coal-fired power production...
Continue reading

Biotechnology and AI: Transforming Agriculture and Sustainability
The world is facing an unprecedented challenge of feeding a growing population and dealing with environmental issues. Biotechnology and AI have emerged as disruptive technologies capable of addressing these issues....
Continue reading
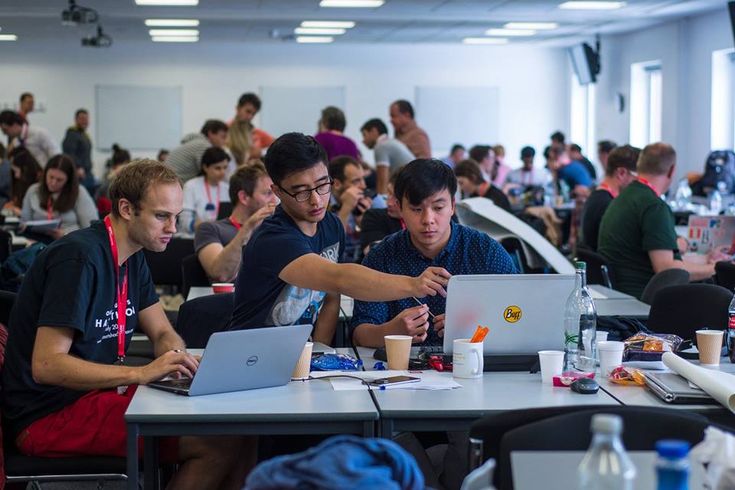

Hackathons: Driving Innovation and Building Future Tech Careers
In the fast lifestyle of the tech world, it’s all about innovation and flexibility. The hackathon is one event that sums up all these qualities. These are collaborative and intensive...
Continue reading

